Event sourcing
Context and problem
Sometimes, we don't just want to see the current state of the data, but also want to know how and what happened to our data. In a traditional database, only the current state of the entity is stored, and the business operation context is usually lost or sometimes stored elsewhere.
Conceptual overview
Event sourcing is pattern for storing data as events.
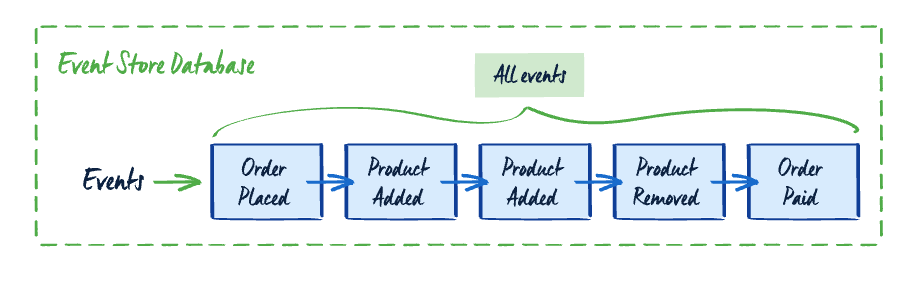
In the context of event sourcing, an event represents a fact that took place within your business. Every change made is stored in the event database. An entity's current state can be created by replaying all the events in the order of occurrence.
Here's an example of events in an event sourcing system
Projection
A projection provides a view of the underlying event-based data model. Often, they represent the logic of translating the source write model into a read model. A common scenario is taking events created in the write model (OrderCreated, OrderAllocated, ...) and calculating a read model view (Order object containing the total amount, user purchased order, and a list of product items in the order). This type of object can be stored in a different database and used for queries.
Subscription
It's a similar concept to Change Data Capture in relational databases. Each event inserted into the database can trigger a notification, and subscribers can listen to those notifications. Some cases where this feature can be useful are:
- Run a projection to update read model
- Forward the event to message queues or external services.
Code details
Event sourcing pattern can be checked in order service.
Write model
- In the command handler of CQRS pattern, an event is published to the state machine, which implements the Saga pattern
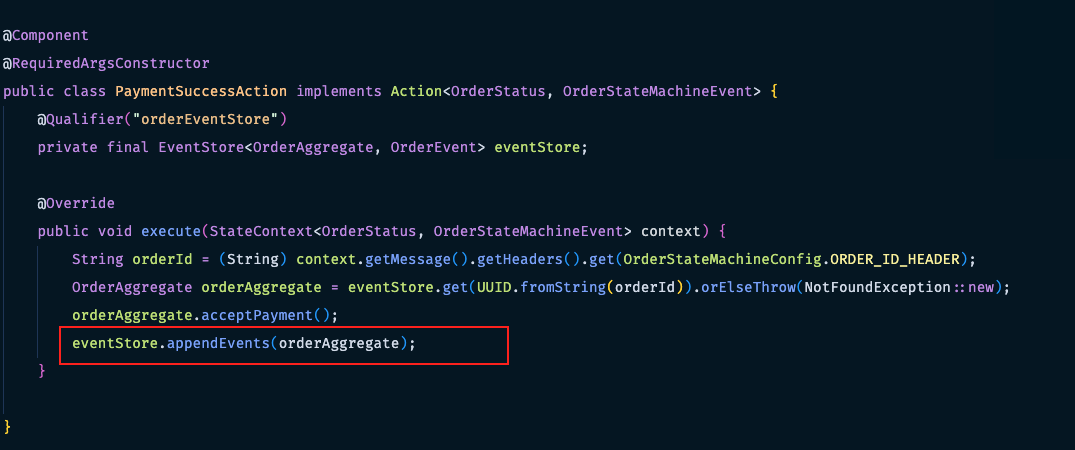
- When the state of machine is transitioned to a new state (e.g. from
PAYMENT_PENDINGtoPAIDorPAYMENT_EXCEPTION), an action will be fired. - When an action is fired, events will stored in eventstore database.
Read model
- Read models are rebuilt with subscribe to $all stream feature of EventStoreDB. The subscription code can be found under
order-service/src/main/java/eshop/orderservice/core/subscription/EventStoreDBSubscriptionToAll.java - EventStoreDB subscription forwards event to Spring Boot Application Event Publisher
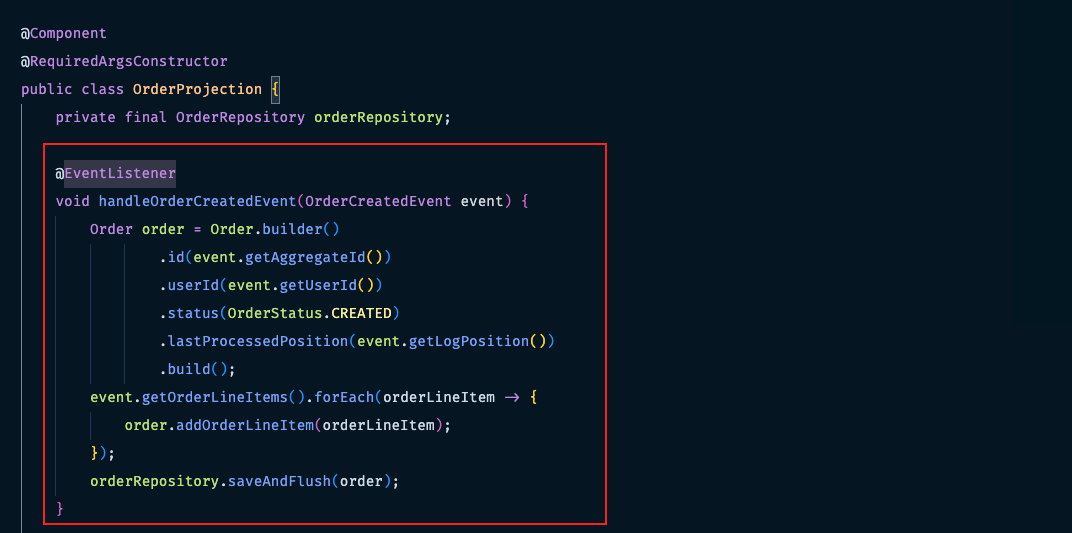
- The
projectionwill listen to those spring boot events and store projection data into Postgres table by usingSpring data JPA. Theprojectioncode can be found underorder-service/src/main/java/eshop/orderservice/order/projection/OrderProjection.java. Here is example of an event listener in projection